Previously I blogged about the difference between integrated first person shooters (FPS) and flight simulators, and how these differences mean that FPS tend to adopt new graphics technology significantly ahead of flight simulators. One of the major differences is that a FPS often will have its content packaged with the rendering engine in a single, unified product, while a general purpose flight simulator is expected to cope with third party content.
The need to be a platform for external content doesn’t just impact our ability to optimize for “special cases” (e.g. we can’t assume anything about third party); it also puts more pressure on the rendering engine to be robust in the case of error.
X-Plane has low level and high level scenery abstractions.
- Low level: an OBJ is low level. You give us a textured mesh, and we draw it. We don’t process the mesh, we don’t interpret it, we just draw what you made in Blender, AC3D, etc.
- High level: a forest. You tell us the outline of the forest’s area and give us some trees and we fill in the forest, picking trees and placing them.
Now there is always the risk that third party content can look stupid. If you model an airplane and you use 4 quads for each engine, your airplane is going to look bad, and there’s nothing the rendering engine can do to fix that.
But with higher level abstractions, the problem is more subtle. If the input data to a high level abstraction has a problem, X-Plane’s rendering might look bad. But what constitutes a problem?
In the case of forests, if the polygonal area of a forest is too thin (along certain axes) we will fail to put any trees into the polygon. Exactly what represents too thin isn’t particularly well documented or even easy to measure. This is difficult for third parties, because they don’t have an explicit set of guidelines for “you will make the rendering engine grumpy if you do X.”
This is the kind of thing that, in an integrated FPS, is much easier to cope with. The art team tries a technique, and if it looks bad, they email the rendering engine coder. The coders then either fix the rendering engine or tell the artist “don’t do that”.
In our case, we need to be more robust in the case of input data problems because we can’t tell everyone who tries X-Plane “don’t do that”, particularly when the edge cases may change with rendering engine improvements. So whereas a rendering engine feature in an integrated FPS might be useful if it looks good when used in a few usage cases , a rendering engine feature in X-Plane is only useful when it looks good under most usage cases.
This is two pictures of “tilings” of OpenStreetMap for use in global scenery. I downloaded a OSM new planet extract about a month ago; in the 11 months since I last grabbed it, the data size has grown 56%! The new, larger file required some changes to my extracting code. After much debugging, I was able to see this in QGIS:
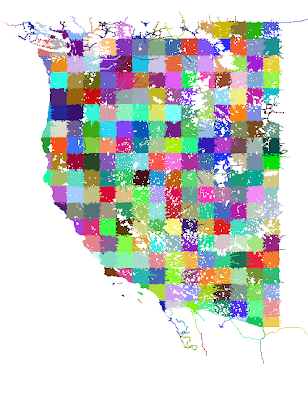
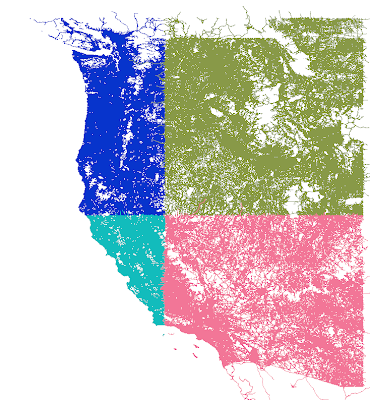
The first picture is 1×1 tiles, which are derived from the second picture (10x10s). You’ll see some “ragged” edges. This is because the cutting scheme leaves whole roads of interest in one piece even outside the tiling bounds. Later, more sophisticated code crops the road when the actual DSF is built.
The OSM processing tools are part of the open source scenery tools; I will get my changes checked in to source control over the next few days, although my code is only one of dozens of programs for bulk processing OSM.
I’ve been working on road processing today; one of the tricky problems with OSM data is that, because an OSM map is often a collection of vectors from separate authors, the results can be a huge number of very small segments, as nearby road features from different data sources cross each other. (Basically you get “thrash” between the two vectors from different sources and our tools solve this by adding a huge number of extra vertices.)
I am trying to run this data through an algorithm called Iterative Snap Rounding (ISR) to reduce this mess of vertices, and for the purpose of this blog article there’s one thing you need to know about ISR: it is really, really slow. So for the next few minutes, I figured I’d start poking at some of the issues that came up at the X-Plane Congress in France this summer.
One question that came up was whether/when X-Plane will go 64 bit. Here’s my current thinking:
We can’t drop 32-bit X-Plane. Too many users have a 32 bit operating system, or a 32-bit CPU. One thing I have been resisting for X-Plane 10 is a ratcheting up of the system requirements to only top-end game machines. While 64 bit is becoming more prevalent and has the potential to be a big win for users who load the sim up with third party add-ons and have a high-end graphics card, plenty of people buy a computer first and then discover X-Plane. Those users will often have a system that is low end (by X-Plane standards).
If we start cranking the system requirements (you have to have 64-bit, you have to have a DX10 class graphics card, you have to have 2 GB of RAM) then more users who might discover X-Plane won’t even be able to run the demo, and that will be bad for X-Plane’s growth.
So the question is not “when will we switch from 32-to-64 bit” – it is “when will we support both 32 and 64 bit.”
I think we will get there during the version 10 run, but I don’t think it’s that likely that we’ll ship 64 bit right out of the box. 64 bit is more of a performance enhancement* than a new feature. The features we have strong motivation to get into 10.0 are:
- Anything that raises the system requirements, because we don’t want to raise system requirements after we ship in a free update.
- Anything that enhances the authoring SDK, where it might be useful for authors to know that every version of X-Plane 10 has a feature.
- Of course, we want to ship any feature that looks really good and gets people excited.
- Foundation features that support other featuers have to go in first. So some enhancements that will ship in 10.0 are there because without them other tech couldn’t be rolled out.
64 bit is important, but it is a feature that only helps some of the user base, and helps by making the sim more expandable; the sim is still usable without it. So we’ll get there, but new features are a zero sum game so I think 64 bit is more likely to be a free patch than in-the-box.
(At this point I expect the various 64-bit OS users who have been asking for a 64-bit app for years to flame the heck out of me and point out that I am a cranky old bastard who doesn’t realize that 64 bit is now everywhere and totally pervasive and that this is therefore the most important thing we could possibly do. Before you dig in, hang on one second, let me put on my asbestos flame-retardant jacket. Okay…fire away. 🙂
Oops…ISR just finished…with a seg fault. Gotta go!
* As a performance enhancement, 64 bit is a weird one; because a 64-bit app uses more memory for pointer-based structures, the same data structures become larger, thrashing on-chip caches more. The real benefit to 64 bits is to allow X-Plane to use more than 3 GB of physical RAM.
To put it mildly, I am buried. If you have emailed me in the last few weeks, I apologize, but basically whatever is going on, I can’t look at it for at least a few more weeks. The four posts for June is an indication of work-load. In particular, since a lot of what I am working on is v10, it is under the radar until we do some kind of more formal announcements.
I did find a little bit of time last night to fix a MeshTool bug (thanks to the users who found this – it was a tricky one!). There will be a MeshTool RC2 to fix the bug: if you use only “wet” orthophotos (that is, orthophotos that have water-like physics) but not “dry” ones, the orthophotos are not exported at all.
I realize that the entire schema for creating mixed wet/dry orthophotos in MeshTool is byzantine at best. Basically you have to manually build the set of GIS files to create this effect, and even with examples in the README it is still pretty hard to do. I hope to automate this a bit in a future version of MeshTool but for now I need to finish version 2.0 as is. I’ll try to cut a new RC within the week.
Also a slight side note: MeshTool contains some hidden commands to let you build road grids inside MeshTool. This was never documented or supported; the code came from a merge of Andrew McGreggor’s work on New Zealand. Starting with RC2, exporting roads will simply not do anything.
The problem is that I did not separate MeshTool from the rest of the scenery code, and the rest of the scenery code is transitioning toward version 10 roads (which do you no good now as v10 isn’t released). If you are successfully using the hidden road code in MeshTool, email me and I can advise you on how to cut your own build. If you are trying to use the hidden road code but not succeeding, please use another tool like Jonathan Harris’ XPOSM.
In the long term we will end up with “draped” roads in overlays – that is, roads that do not depend on the shape of the mesh. Thus you will be able to simply write road data into an overlay file (or someday draw it in WorldEditor). But we’re not there yet.
Tyler has made a lot of progress moving the scenery documentation to the wiki. Once I find some time to give him more feedback we will be able to complete this process. Hopefully this will make it easier to keep the documentation updated.
A few years ago I blogged about gamma correction for png files. Here’s the very, very short version:
- PC and Mac monitors are calibrated differently. Dark tones on a PC appear darker than on a Mac. The curve of how colors are mapped to the monitor is the gamma correction curve, typically expressed as a number like 1.8 for Mac and 2.2 for PC. The higher the number, the more Gothic your dark tones.
- A png file can have a gamma value written into the file, which tells X-Plane (and anyone else) what kind of monitor the png was drawn on. This lets X-Plane brighten a png from a Mac when you are on a PC, and darken a png from a PC when you are on a Mac.
- If you leave off the gamma value on your png, we assume 1.8 (Mac) which can be bad if you’re a PC author.
While this is confusing, it was an improvement over the BMP situation (where everything was set up for a Mac and PC users had to simply crank their monitor brightness).
In version 9 we added a gamma correction setting to X-Plane. The setting you enter in the rendering settings is how “dark” your monitor is (bigger number = darker). We then attempt to compensate by lightening the textures more; thus a bigger number results in a lighter looking X-Plane (because you told us your monitor was dark and we tried to “fix it”).
There are two other developments since the original png situation which have unfortunately been a step backward in terms of X-Plane color correction.
DDS and Gamma
The handling of DDS and gamma is, to put it mildly, quite problematic. The problem is two-fold:
- DDS doesn’t actually have gamma information, so we can’t tag DDSes as having originated on Macs and PCs. So we assume a DDS is authored at a gamma of 1.8 (Mac). I think DDSTool correctly does a gamma correction when grinding files at other gammas.
- (If you are a real graphics programmer, please do not read this next sentence.) X-Plane attempts to adjust the color of the DDS in its compressed form. This is a big hack designed to keep framerate high, but it’s really not a very good idea. The result can be color distortion when a DDS is viewed at 2.2 gamma.
So that’s not good, but what happened next made things a lot worse.
Apple Goes Gothic
Apple adopted the sRGB color profile for OS X 10.6, which has a gamma curve of about 2.2. So now the situation with DDS is particularly ugly:
- All DDS are authored at a gamma of 1.8.
- All users are moving toward a display gamma of 2.2.
- X-Plane thus has to always color correct, but its color correction is low quality for performance reasons.
This is…very sad.
There are two things we can do about this:
- In the short term, we can provide post-decompression color correction. This will cost a (hopefully) small amount of framerate and improve color fidelity for users with 2.2 gamma. This is the kind of thing that any user with a modern card would want, but that we might make optional for users with very old hardware.
- In the long term, we can provide a gamma calibration in the text files that wrap DDS files so that authors can mark their DDS as already being 2.2. This will mean that for most users X-Plane won’t have to do any color correction at all.
There were a few threads regarding lighting rheostats in X-Plane 9. Here’s a short version of the issue and why we’re not changing X-Plane 9’s behavior.
X-Plane 9’s policy toward lighting rheostats is a little bit arbitrary. The sim will pre-position every lighting rheostat in the cockpit to 75% intensity on sim startup, and from that point on, we never touch them. We do not reset them when you load a new plane or reset your flight.
The result of this is that when you load a new airplane, it “inherits” the rheostat positions of the last airplane loaded. This can cause a problem if the newly loaded plane doesn’t have controls to adjust the lights (e.g. it has no instruments on the 2-d panel or manipulators on the 3-d panel, and there is no keyboard shortcut defined). A plane can be “stuck dark”.
It would be nice if X-Plane would pre-initialize the lighting rheostats on startup, but X-Plane deos not have enough information to do this. For example, on plane load, the instrument brightness should be set fairly high (so a glass cockpit can be read during the day) but the flood lights should be fairly low (to prevent loss of night vision). But X-Plane has no idea which rheostats control instruments and which control floods. So if we wanted to correctly initialize the cockpit, we wouldn’t have enough information.
To make it more complicated, some airplane authors have taken it upon themselves to initialize the cockpit via plugin code. If X-Plane were to start changing the rheostats at startup, it might undo some of what these plugins have done.
Given the difficulty of maintaining compatibility and the lack of a “correct” set of values, we decided not to change the behavior in 9.50 or 9.55.
If there’s any take-away point for airplane authors, I think it is this: provide controls for the lighting rheostats that you use in your airplane. Otherwise the user can’t turn the lights on if they are off for any reason. You can control the lighting rheostats with a generic instrument, manipulator, or the built-in instruments.
Ugly Glow
There is a separate issue that sometimes comes up: X-Plane panels can look bad when the flood lights are turned all the way up during the day. A panel can look very red and washed out, for example.
This problem comes from a mismatch of real-world lighting levels. In the real world, the sun is approximately four gajillion times more powerful than the little dome lights in an airplane. So when the sun is out, the dome light isn’t visible even if it’s turned all the way up. The dome light only looks bright when your eyes have adjusted to a no-sun condition.
What X-Plane should do (and may do in the future) is scale all cockpit lights relative to the overall daytime brightness, which would effectively dim the effect of flood lights during the day. Simply turning down flood lights when a flight is started during the day is not a full solution, as the user can simply turn them right back up again and end up with an unrealistic scene.
Suffice it to say, I think we will address these things in a v10 time frame, not a v9 time frame; in the short term it’s better to have airplanes continue to function as the author intended.
We have Tyler working for us again for the summer (last summer he did a very nice and much needed rework of the X-Plane manual), and among his projects is cleaning up the mess that is scenery documentation.
We are moving the scenery documentation from their own dedicated site to the X-Plane wiki. As of this writing, as you can tell, it’s a work in progress. There are a few reasons why we decided to consolidate to the wiki:
- The scenery website is the very best of 1995 technology – unmanaged php in a big mess of files. We wanted to get the site under some kind of content management system, and MediaWiki is already working well for us for other docs.
- There is a lot of overlap between modeling techniques for scenery and modeling techniques for airplanes, so having all of the third party authoring docs in one place makes sense.
It’ll be a few more weeks before everything is organized.
Tyler is also reviewing all of the documentation. I have had a lot of trouble trying to document the scenery system, partly because I have been working on it for years, and thus I have no sense of what people don’t know. Since Tyler hadn’t done any scenery work before, he was able to read the documents and go “hey Ben, you keep talking about X but you never defined what it is.” The resulting edits should make the docs a lot clearer.
In order to understand the difference between hiding geometry and disabling drawing, you need to understand that an OBJ triangle can serve many purposes. Broadly, those purposes are:
- Drawing (the most basic use).
- Collision detection, of which we have three flavors: collision of the plane with the object (“hard surfaces”, or “physics”), collision of the mouse with the panel (manipulators, or clickable triangles) and collisions of the camera with the airplane (“solid camera”, which constrains the camera).
Any given triangle can be drawn and/or used to check for any of these collisions*; attributes change what the triangle is used for.
By default, all triangles are drawn; ATTR_draw_disable marks future triangles as not being drawn. This allows you to make a triangle that is used only for collisions. Examples might include a “hot spot” in front of a region on the panel (the hot spot might be easier to click than a small switch) and an invisible simple mesh to constrain the camera.
By comparison, ANIM_hide effectively removes some triangles from your model (temporarily) for all uses – drawing and collision detection of any kind. If a door is hidden, it’s not only not drawn, but it’s not going to stop the camera moving through it either.
Some key points to these distinctions:
- Categorizing what a triangle is used for (drawing, various flavors of collisions) is static – that is, it is always the same for the object and never changes with datarefs or animation. This is intentional for performance reasons!
- Animation to hide triangles affects the triangle in every way consistently – drawing and collisions.
Generally, you will get better performance improvements by removing categories from a triangle than by hiding it. (That is, it is better to not have manipulators on your cockpit, so it isn’t mouse-click collision-checked, than to hide it.) But the purpose of ATTR_draw_disable and ANIM_hide are different enough that which you use will be determined by the effect you are trying to create.
Finally, note that hiding an object completely (that is, the object does no drawing) does not provide the maximum performance benefit of not having an object at all. ANIM_hide was created to allow authors to create clever effects, not as a performance enhancer!
* This is not quite accurate: airplane-object collision checks are only available in scenery objects, and camera/airplane or mouse/panel collision checks are only available in the cockpit object.
I was discussing plugin-controlled prop discs with a third party developer. The developer wanted to know if custom prop disc control would end up inside Plane-Maker. It may end up doing so, but I don’t think this would be nearly as useful as it would seem. What follows is my explanation to him of why this is.
Let me draw an analogy: when it comes to systems modeling, using a plugin is to Plane-Maker as using Blender is to using Plane-Maker.
Users who cannot use Blender are frustrated because they cannot make something as nice as those who are building planes out of OBJs. Sometimes they ask for more features in Plane-Maker, like: more stations! This new editing mode! Make the UI better!
But…you tell me: will Plane-Maker’s UI ever be as flexible and powerful as Blender? And if it ever did get to be that good, would that have turned out to be a good use of LR’s time, when Blender is already available?
The motivation for OBJ-based airplane geometry via third party tools is that what users want to do cannot be easily generalized into a few simple cases. Every plane is different, so a truly flexible platform is needed.
The prop disc (and other systems modeling problems) are the same way. In developing the prop disc graphics, I spoke with a number of third party developers who had already tried to push prop discs as far as they could go, were using plugins, were drawing themselves, as well as 25 other crazy hacks. I also spoke to our internal art team. And what I found was: no one had any consensus on how the prop disc system should work. Everyone wanted to tune a very specific set of behaviors to their peculiar art assets.
That’s what drove me to put it into a plugin. When we need an equation or a strategy we reach the point where we need more flexibility than Plane-Maker can exhibit. A plugin can encapsulate a strategy or technique in a way that Plane-Maker radio buttons cannot.
Consider what would happen if custom prop disc parameters were built into Plane-Maker. Everyone would have to wait until Austin implemented the prop disc algorithm they wanted. How would this be bad? Let me count the ways?
- How many algorithms do you think Austin has time to code? Not more than he has fingers on his right hand. Only the five lucky third party developers who get their algorithm coded will be happy with this.
- Austin code exactly what you want? Don’t get your hopes up.
- , what you asked for wasn’t what you wanted? We can’t change the behavior now, that would break compatibility!
- oh…your email got eaten by a spam filter? Too bad…no custom prop disc for you!
- Sorry, we don’t have a release vehicle lined up for the next 3 months. You’ll have to wait.
This problem is already happening across pretty much every aspect of systems modeling: airplane have unique, quirky systems which are usually useful for exactly one plane. It is not even remotely sustainable for X-Plane to code these things one at a time with a set of check-boxes. We might as well have a pop-up menu for every airplane ever invented, and simulate every single airplane inside the sim itself. Imagine the development costs…if a single high quality MSFS add-on sells for $30-$50…
Think of the prop disc via plugins situation (and the strobe lights are the same way) as an experiment in generic instruments for systems. By transitioning to a generic abstaction for instruments we’ve let a lot more users do exactly what they want with a small, high performance piece of code. The original instrument strategy (one of everything) reached a point where we simply couldn’t meet user needs in a cost-effective manner.
In X-Plane there are two fundamental ways that a texture can be painted “over” a background image:
- Blending, whereby the alpha channel of the new top layer decides how much we see the top layer vs. the background.
- Additive Lighting, whereby the new texture makes the background lighter.
Blending is more common. For example, if you build an OBJ, the object appears “in front of” the terrain via blending. With blending, you put the color of your new layer in the RGB channels and use the alpha channel to indicate opacity. 1.0 alpha = 100% opaque, 0.0 alpha = 0% opaque, and alpha in between will create a blend. If you omit an alpha channel, X-Plane will treat the entire layer as 100% opaque.
When a layer is applied using additive lighting, the resulting color is the sum of the background plus the new color, clamped to the maximum brightness we can show on screen. Additive lighting is good for simulating effects that really “add light”. Some examples of additive lighting in X-Plane:
- All lighting billboards are drawn additively.
- Instrument overlays are additive if you pick the appropriate mode in Plane-Maker. (The option is labeled “glass” for generics, since most glass instruments work by adding light to a nearly black screen.)
- The emissive (_lit) texture of an object is added to the albedo (daytime) texture using additive lighting.
Now just a little bit of math. In RGB color terms, black = 0,0,0 and white = 1,1,1. So if we add a pure black texture to a background additively we get:
new_r = old_r + overlay = old_r + 0 = old_r
new_g = old_g + overlay = old_g + 0 = old_g
new_b = old_b + overlay = old_b + 0 = old_b
In other words,when using additive light, adding “black” does nothing, preserving the background.
And this brings me to my main point: any time you have additive lighting you don’t need an alpha channel. You can simply make your additive lighting texture black for the parts you want to be “transparent”.
This is why I generally recommend that emissive _LIT textures for objects not have an alpha channel. In fact, for “back-lit” and “additive” instruments (these are instruments that use a second emissive _LIT texture) Plane-Maker will indicate a warning if the texture has an alpha channel. If you have a texture that is applied additively, you don’t need alpha.
At this point you might be wondering: Ben, if additive lighting doesn’t require alpha, and all lighting billboards are drawn additively, why the heck is there an alpha channel for custom lights?
The short answer is: there probably doesn’t need to be one; the original setup for lighting billboards inherited a number of idioms from older versions of X-Plane, going back to versions where lighting billboards were not additive* (and thus alpha was necessary).
The long answer is: the alpha channel is often as a general “intensity” control to turn the light up and down in amplitude, while the RGB channels are often re-interpreted in strange ways. So while RGBA color is not necessary from a graphics standpoint, it is handy that there are four color channels in the custom lights because that gives us one more parameter to play with when designing really compicated lights (like VASIs).
* Note that lighting billboards that aren’t additive don’t look very good…hence Austin switched to additive billboards.

